VIRACEPT Clinical Studies
(nelfinavir mesylate)
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Description of Clinical Studies
The efficacy of VIRACEPT is based on analyses of multiple clinical studies in HIV-1 infected antiretroviral treatment-naïve and experienced adult patients. In the adult clinical studies described below, efficacy was evaluated by the percent of patients with plasma HIV RNA <400 copies/mL (Studies 511 and 542), <500 copies/mL (Study ACTG 364), or <50 copies/mL (Study Avanti 3). In the analysis presented in each figure, patients who terminated the study early for any reason, switched therapy due to inadequate efficacy or who had a missing HIV-RNA measurement that was either preceded or followed by a measurement above the limit of assay quantification were considered to have HIV-RNA above 400 copies/mL, above 500 copies/mL, or above 50 copies/mL at subsequent time points, depending on the study's definition of virologic failure.
14.1 Studies in Antiretroviral Treatment Naïve Adult Patients
Study 511: VIRACEPT + zidovudine + lamivudine versus zidovudine + lamivudine
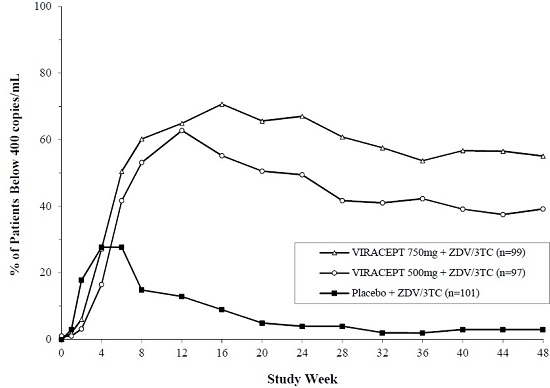
Study 511 is a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial comparing treatment with zidovudine (ZDV; 200 mg TID) and lamivudine (3TC; 150 mg BID) plus 2 doses of VIRACEPT (750 mg and 500 mg TID) to zidovudine (200 mg TID) and lamivudine (150 mg BID) alone in 297 antiretroviral naïve HIV-1 infected patients. The median age was 35 years [range 21 to 63]; 89% were male and 78% were Caucasian. Mean baseline CD4 cell count was 288 cells/mm3 and mean baseline plasma HIV RNA was 5.21 log10 copies/mL (160,394 copies/mL). The proportion of patients with plasma HIV RNA <400 copies/mL at Week 48 was 86%, as summarized in Figure 1. The mean change in CD4 cell count at Week 48 was 207.6 cells/mm3.
Figure 1
Study 511: Percentage of Patients With HIV RNA Below 400 Copies/mL
Study 542: VIRACEPT BID + stavudine + lamivudine compared to VIRACEPT TID + stavudine + lamivudine
Study 542 is a, randomized, open-label trial comparing the HIV RNA suppression achieved by VIRACEPT 1250 mg BID versus VIRACEPT 750 mg TID in patients also receiving stavudine (d4T; 30–40 mg BID) and lamivudine (3TC; 150 mg BID). Patients had a median age of 36 years (range 18 to 83), were 84% male, and were 91% Caucasian. Patients had received less than 6 months of therapy with nucleoside transcriptase inhibitors and were naïve to protease inhibitors. Mean baseline CD4 cell count was 296 cells/mm3 and mean baseline plasma HIV RNA was 5.0 log10 copies/mL (100,706 copies/mL).
Results showed that there was no significant difference in mean CD4 cell count among treatment groups; the mean increases from baseline for the BID and TID arms were 150 cells/mm3 at 24 weeks and approximately 200 cells/mm3 at 48 weeks.
The percent of patients with HIV RNA <400 copies/mL and the outcomes of patients through 48 weeks of treatment are summarized in Table 14.
| Outcome | VIRACEPT 1250 mg BID Regimen | VIRACEPT 750 mg TID Regimen |
|---|---|---|
| ||
Number of patients evaluable* | 323 | 192 |
HIV-1 RNA <400 copies/mL | 198 (61%) | 111 (58%) |
HIV-1 RNA ≥400 copies/mL | 46 (14%) | 22 (11%) |
Discontinued due to VIRACEPT toxicity† | 9 (3%) | 2 (1%) |
Discontinued due to other antiretroviral agents' toxicity† | 3 (1%) | 3 (2%) |
Others‡ | 67 (21%) | 54 (28%) |
Study Avanti 3: VIRACEPT TID + zidovudine + lamivudine compared to zidovudine + lamivudine
Study Avanti 3 was a placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of VIRACEPT (750 mg TID) in combination with zidovudine (ZDV; 300 mg BID) and lamivudine (3TC; 150 mg BID) (n=53) versus placebo in combination with ZDV and 3TC (n=52) administered to antiretroviral-naïve patients with HIV infection and a CD4 cell count between 150 and 500 cells/μL. Patients had a mean age of 35 (range 22–59), were 89% male, and 88% Caucasian. Mean baseline CD4 cell count was 304 cells/mm3 and mean baseline plasma HIV RNA was 4.8 log10 copies/mL (57,887 copies/mL). The percent of patients with plasma HIV RNA <50 copies/mL at 52 weeks was 54% for the (VIRACEPT + ZDV + 3TC)-treatment group and 13% for the (ZDV + 3TC)-treatment group.
14.2 Studies in Antiretroviral Treatment Experienced Adult Patients
Study ACTG 364: VIRACEPT TID + 2NRTIs compared to efavirenz + 2NRTIs compared to VIRACEPT + efavirenz + 2NRTIs
Study ACTG 364 was a randomized, double-blind study that evaluated the combination of VIRACEPT 750 mg TID and/or efavirenz 600 mg QD with 2 NRTIs (either didanosine [ddI] + d4T, ddI + 3TC, or d4T + 3TC) in patients with prolonged prior nucleoside exposure who had completed 2 previous ACTG studies. Patients had a mean age of 41 years (range 18 to 75), were 88% male, and were 74% Caucasian. Mean baseline CD4 cell count was 389 cells/mm3 and mean baseline plasma HIV RNA was 3.9 log10 copies/mL (7,954 copies/mL).
The percent of patients with plasma HIV RNA <500 copies/mL at 48 weeks was 42%, 62%, and 72% for the VIRACEPT (n=66), EFV (n=65), and VIRACEPT + EFV (n=64) treatment groups, respectively.
14.3 Studies in Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetic profile, safety and antiviral activity of VIRACEPT in pediatric patients 2 years of age up to 13 years were evaluated in 2 randomized studies.
Study 556 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with VIRACEPT or placebo coadministered with ZDV and ddI in 141 HIV-positive children who had received minimal antiretroviral therapy. The mean age of the children was 3.9 years. Ninety four (67%) children were between 2–12 years, and 47 (33%) were < 2 years of age. The mean baseline HIV RNA value was 5.0 log for all patients and the mean CD4 cell count was 886 cells/mm3 for all patients. The efficacy of VIRACEPT measured by HIV RNA <400 at 48 weeks in children ≥2 years of age was 26% compared to 2% of placebo patients (p=0.0008). In the children < 2 years of age, only 1 of 27 and 2 of 20 maintained an undetectable HIV RNA level at 48 weeks for placebo and VIRACEPT patients, respectively.
PACTG 377 was an open-label study that randomized 181 HIV treatment-experienced pediatric patients to receive: d4T+NVP+RTV, d4T+3TC+NFV, or d4T+3TC+NVP+NFV with NFV given on a TID schedule. The median age was 5.9 years and 46% were male. At baseline the median HIV RNA was 4.4 log and median CD4 cell count was 690 cells/mm3. Substudy PACTG 725 evaluated d4T+3TC+NFV with NFV given on a BID schedule. The proportion of patients with detectable viral load at baseline achieving HIV RNA <400 copies/mL at 48 weeks was: 41% for d4T+NVP+RTV, 42% for d4T+3TC+NFV, 30% for d4T+NVP+NFV, and 52% for d4T+3TC+NVP+NFV. No significant clinical differences were identified between patients receiving VIRACEPT in BID or TID schedules.
VIRACEPT has been evaluated in 2 studies of young infants. The PENTA 7 study was an open-label study to evaluate the toxicity, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and activity of NFV+d4T+ddI in 20 HIV-infected infants less than 12 weeks of age. PACTG 353 evaluated the pharmacokinetics and safety of VIRACEPT in infants born to HIV-infected women receiving NFV as part of combination therapy during pregnancy.
The following issues should be considered when initiating VIRACEPT in pediatric patients:
- •
- In pediatric patients ≥2 years of age receiving VIRACEPT as part of triple combination antiretroviral therapy in randomized studies, the proportion of patients achieving a HIV RNA level <400 copies/mL through 48 weeks ranged from 26% to 42%.
- •
- Response rates in children <2 years of age appeared to be poorer than those in patients ≥2 years of age in some studies.
- •
- Highly variable drug exposure remains a significant problem in the use of VIRACEPT in pediatric patients. Unpredictable drug exposure may be exacerbated in pediatric patients because of increased clearance compared to adults and difficulties with compliance and adequate food intake with dosing. Pharmacokinetic results from the pediatric studies are reported in Table 11 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The pharmacokinetic profile, safety and antiviral activity of VIRACEPT in adolescent patients 13 years and older is supported by data from the adult clinical trials where some trials allowed enrolment of subjects 13 years and older. Thus, the data for adolescents and adults were analyzed collectively.
Find VIRACEPT medical information:

Find VIRACEPT medical information:
VIRACEPT Quick Finder
Health Professional Information
Clinical Studies
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Description of Clinical Studies
The efficacy of VIRACEPT is based on analyses of multiple clinical studies in HIV-1 infected antiretroviral treatment-naïve and experienced adult patients. In the adult clinical studies described below, efficacy was evaluated by the percent of patients with plasma HIV RNA <400 copies/mL (Studies 511 and 542), <500 copies/mL (Study ACTG 364), or <50 copies/mL (Study Avanti 3). In the analysis presented in each figure, patients who terminated the study early for any reason, switched therapy due to inadequate efficacy or who had a missing HIV-RNA measurement that was either preceded or followed by a measurement above the limit of assay quantification were considered to have HIV-RNA above 400 copies/mL, above 500 copies/mL, or above 50 copies/mL at subsequent time points, depending on the study's definition of virologic failure.
14.1 Studies in Antiretroviral Treatment Naïve Adult Patients
Study 511: VIRACEPT + zidovudine + lamivudine versus zidovudine + lamivudine
Study 511 is a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial comparing treatment with zidovudine (ZDV; 200 mg TID) and lamivudine (3TC; 150 mg BID) plus 2 doses of VIRACEPT (750 mg and 500 mg TID) to zidovudine (200 mg TID) and lamivudine (150 mg BID) alone in 297 antiretroviral naïve HIV-1 infected patients. The median age was 35 years [range 21 to 63]; 89% were male and 78% were Caucasian. Mean baseline CD4 cell count was 288 cells/mm3 and mean baseline plasma HIV RNA was 5.21 log10 copies/mL (160,394 copies/mL). The proportion of patients with plasma HIV RNA <400 copies/mL at Week 48 was 86%, as summarized in Figure 1. The mean change in CD4 cell count at Week 48 was 207.6 cells/mm3.
Figure 1
Study 511: Percentage of Patients With HIV RNA Below 400 Copies/mL
Study 542: VIRACEPT BID + stavudine + lamivudine compared to VIRACEPT TID + stavudine + lamivudine
Study 542 is a, randomized, open-label trial comparing the HIV RNA suppression achieved by VIRACEPT 1250 mg BID versus VIRACEPT 750 mg TID in patients also receiving stavudine (d4T; 30–40 mg BID) and lamivudine (3TC; 150 mg BID). Patients had a median age of 36 years (range 18 to 83), were 84% male, and were 91% Caucasian. Patients had received less than 6 months of therapy with nucleoside transcriptase inhibitors and were naïve to protease inhibitors. Mean baseline CD4 cell count was 296 cells/mm3 and mean baseline plasma HIV RNA was 5.0 log10 copies/mL (100,706 copies/mL).
Results showed that there was no significant difference in mean CD4 cell count among treatment groups; the mean increases from baseline for the BID and TID arms were 150 cells/mm3 at 24 weeks and approximately 200 cells/mm3 at 48 weeks.
The percent of patients with HIV RNA <400 copies/mL and the outcomes of patients through 48 weeks of treatment are summarized in Table 14.
| Outcome | VIRACEPT 1250 mg BID Regimen | VIRACEPT 750 mg TID Regimen |
|---|---|---|
| ||
Number of patients evaluable* | 323 | 192 |
HIV-1 RNA <400 copies/mL | 198 (61%) | 111 (58%) |
HIV-1 RNA ≥400 copies/mL | 46 (14%) | 22 (11%) |
Discontinued due to VIRACEPT toxicity† | 9 (3%) | 2 (1%) |
Discontinued due to other antiretroviral agents' toxicity† | 3 (1%) | 3 (2%) |
Others‡ | 67 (21%) | 54 (28%) |
Study Avanti 3: VIRACEPT TID + zidovudine + lamivudine compared to zidovudine + lamivudine
Study Avanti 3 was a placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of VIRACEPT (750 mg TID) in combination with zidovudine (ZDV; 300 mg BID) and lamivudine (3TC; 150 mg BID) (n=53) versus placebo in combination with ZDV and 3TC (n=52) administered to antiretroviral-naïve patients with HIV infection and a CD4 cell count between 150 and 500 cells/μL. Patients had a mean age of 35 (range 22–59), were 89% male, and 88% Caucasian. Mean baseline CD4 cell count was 304 cells/mm3 and mean baseline plasma HIV RNA was 4.8 log10 copies/mL (57,887 copies/mL). The percent of patients with plasma HIV RNA <50 copies/mL at 52 weeks was 54% for the (VIRACEPT + ZDV + 3TC)-treatment group and 13% for the (ZDV + 3TC)-treatment group.
14.2 Studies in Antiretroviral Treatment Experienced Adult Patients
Study ACTG 364: VIRACEPT TID + 2NRTIs compared to efavirenz + 2NRTIs compared to VIRACEPT + efavirenz + 2NRTIs
Study ACTG 364 was a randomized, double-blind study that evaluated the combination of VIRACEPT 750 mg TID and/or efavirenz 600 mg QD with 2 NRTIs (either didanosine [ddI] + d4T, ddI + 3TC, or d4T + 3TC) in patients with prolonged prior nucleoside exposure who had completed 2 previous ACTG studies. Patients had a mean age of 41 years (range 18 to 75), were 88% male, and were 74% Caucasian. Mean baseline CD4 cell count was 389 cells/mm3 and mean baseline plasma HIV RNA was 3.9 log10 copies/mL (7,954 copies/mL).
The percent of patients with plasma HIV RNA <500 copies/mL at 48 weeks was 42%, 62%, and 72% for the VIRACEPT (n=66), EFV (n=65), and VIRACEPT + EFV (n=64) treatment groups, respectively.
14.3 Studies in Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetic profile, safety and antiviral activity of VIRACEPT in pediatric patients 2 years of age up to 13 years were evaluated in 2 randomized studies.
Study 556 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with VIRACEPT or placebo coadministered with ZDV and ddI in 141 HIV-positive children who had received minimal antiretroviral therapy. The mean age of the children was 3.9 years. Ninety four (67%) children were between 2–12 years, and 47 (33%) were < 2 years of age. The mean baseline HIV RNA value was 5.0 log for all patients and the mean CD4 cell count was 886 cells/mm3 for all patients. The efficacy of VIRACEPT measured by HIV RNA <400 at 48 weeks in children ≥2 years of age was 26% compared to 2% of placebo patients (p=0.0008). In the children < 2 years of age, only 1 of 27 and 2 of 20 maintained an undetectable HIV RNA level at 48 weeks for placebo and VIRACEPT patients, respectively.
PACTG 377 was an open-label study that randomized 181 HIV treatment-experienced pediatric patients to receive: d4T+NVP+RTV, d4T+3TC+NFV, or d4T+3TC+NVP+NFV with NFV given on a TID schedule. The median age was 5.9 years and 46% were male. At baseline the median HIV RNA was 4.4 log and median CD4 cell count was 690 cells/mm3. Substudy PACTG 725 evaluated d4T+3TC+NFV with NFV given on a BID schedule. The proportion of patients with detectable viral load at baseline achieving HIV RNA <400 copies/mL at 48 weeks was: 41% for d4T+NVP+RTV, 42% for d4T+3TC+NFV, 30% for d4T+NVP+NFV, and 52% for d4T+3TC+NVP+NFV. No significant clinical differences were identified between patients receiving VIRACEPT in BID or TID schedules.
VIRACEPT has been evaluated in 2 studies of young infants. The PENTA 7 study was an open-label study to evaluate the toxicity, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and activity of NFV+d4T+ddI in 20 HIV-infected infants less than 12 weeks of age. PACTG 353 evaluated the pharmacokinetics and safety of VIRACEPT in infants born to HIV-infected women receiving NFV as part of combination therapy during pregnancy.
The following issues should be considered when initiating VIRACEPT in pediatric patients:
- •
- In pediatric patients ≥2 years of age receiving VIRACEPT as part of triple combination antiretroviral therapy in randomized studies, the proportion of patients achieving a HIV RNA level <400 copies/mL through 48 weeks ranged from 26% to 42%.
- •
- Response rates in children <2 years of age appeared to be poorer than those in patients ≥2 years of age in some studies.
- •
- Highly variable drug exposure remains a significant problem in the use of VIRACEPT in pediatric patients. Unpredictable drug exposure may be exacerbated in pediatric patients because of increased clearance compared to adults and difficulties with compliance and adequate food intake with dosing. Pharmacokinetic results from the pediatric studies are reported in Table 11 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The pharmacokinetic profile, safety and antiviral activity of VIRACEPT in adolescent patients 13 years and older is supported by data from the adult clinical trials where some trials allowed enrolment of subjects 13 years and older. Thus, the data for adolescents and adults were analyzed collectively.
Health Professional Information
{{section_name_patient}}
{{section_body_html_patient}}
Resources
Didn’t find what you were looking for? Contact us.
Chat online with Pfizer Medical Information regarding your inquiry on a Pfizer medicine.
*Speak with a Pfizer Medical Information Professional regarding your medical inquiry. Available 9AM-5PM ET Monday to Friday; excluding holidays.
Submit a medical question for Pfizer prescription products.
Report Adverse Event
Pfizer Safety
To report an adverse event related to the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, and you are not part of a clinical trial* for this product, click the link below to submit your information:
Pfizer Safety Reporting Site*If you are involved in a clinical trial for this product, adverse events should be reported to your coordinating study site.
If you cannot use the above website, or would like to report an adverse event related to a different Pfizer product, please call Pfizer Safety at (800) 438-1985.
FDA Medwatch
You may also contact the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) directly to report adverse events or product quality concerns either online at www.fda.gov/medwatch or call (800) 822-7967.